 |
- Move
- cursor
- over slide
-
- slide
1
- slide
2
- slide
3
- slide
4
- slide
5
- slide
6
- slide
7
- slide
8
|
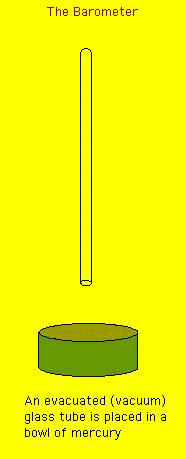
The common barometer simply consists of a bowl of a liquid
(usually mercury) and a glass tube. The glass tube (with a vacuum)
is placed in the mercury. the mercury rises in the tube due to
the gas pressure outside the tube. However, as the mercury rises
its weight within the tube increases until it just balances the
external gas pressure. The resulting height of the mercury is
a direct measure of the external pressure. At sea level the height
of the mercury will be 760 mm. The pressure of air at sea level
is therefore 760 mmHg.
It is possible to make barometers with other liquids than
mercury, however, because of its density mercury is the most
convenient.
|

