 |
- Net Ionic Equation
|
Most reactions in an aqueous medium involve ions. However,
when a reaction takes place two kinds of ions usually emerge:
(1) "spectator" ions and (2) "player" ions.
The names imply the character of the ions with respect to the
reaction. Player ions are directly in the reaction whereas spectator
ions fulfill the role of spectators and their primary function
is keeping electrical neutrality in the solution. Consider the
precipitation reaction that occurs when aqueous solutions of
sodium chloride and silver nitrate are mixed. A white precipitate
of AgCl forms. The chemical equation for this reaction is written
as:

This equation contains all ions in the solution. However,
sometimes its necessary to only include those ions that are players
and leave out the spectators. A chemical equation that contains
only the player ions is called the net ionic equation (nie).
To get the nie (1) write out all soluble compounds as ions and
(2) eliminate ions common to both reactants and products. The
resulting chemical equation is then the nie. For the equation
above we have: (for step 2 move the mouse over the reaction)
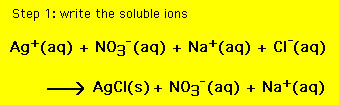
The resulting equation is the net ionic equation,
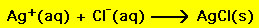
While the above reaction is particularly simple (i.e. all
stoichiometric coefficients are equal to 1), More complex nie's
result from a similar procedure. For example, if iron(III) nitrate
is mixed with ammonium sulfide a yellow precipitate of iron(III)
sulfide results. The nie for this reaction is:
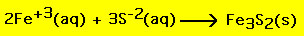
|

