 |
- Solubility of Ionic Compounds
- in Aqueous Solutions
|
When a salt is placed in an aqueous medium (i.e. water) a
"tug-of-war" immediately begins to take place between
the polar water molecules and the ions in the salt. The forces
in the tug-of-war are electrostatic and between the ion-ion attractions
and the water-ion attractions. If the water-ion attraction win
the war then the salt is soluble. If the ion-ion attractions
win then the salt is insoluble. Consider table salt (NaCl), it
is highly soluble and its solubility can be written as
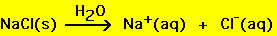
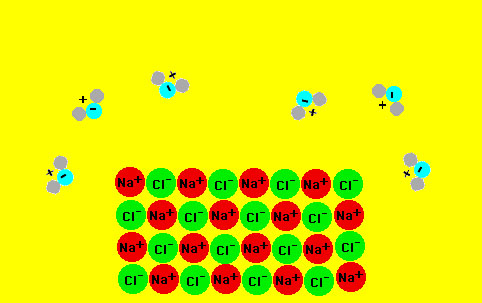
At the atomic level the ions in the salt are being "solvated"
by the water molecules as the animation below suggests (place
mouse over the image). Note the orientation of the water molecules
to the positive and negative ions. The cage of water molecules
around the solvated ion is known as a "hydration" cage.
|

