 |
Compounds
|
There are two basic types of compounds. They are distinguished
by by the manner in which the atoms bind to one another in the
compound. These two types are called "molecular" compounds
and "salts" (or equivalently "ionic" compounds):
| Molecular compounds: |
These compounds are made up
of molecules whose atoms bind to one another through "covalent"
bonds. |
| Salts: |
The atoms in salts are held
together with "ionic" bonds. Unlike molecules, salts
always form solids in a regular array called a "crystalline
solid". |
A bond is the "glue" that holds atoms together.
In compounds this glue can either be covalent or ionic.
| Covalent bonds: |
The electrons are shared
between atoms. Therefore this sharing of electrons provides the
glue. |
| Ionic bonds: |
Ionic bonds occur due to the
mutual attraction between atoms with positive and negative charges
i.e., ions. |
Examples of Molecules
|
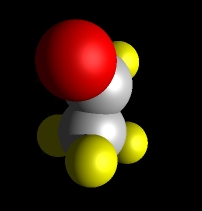
Acetaldehyde
|
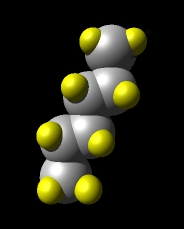
n-hexane
|
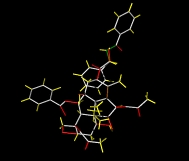 Taxol
Taxol
|
An Example of a Salt
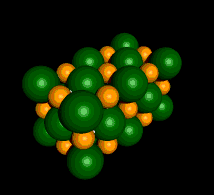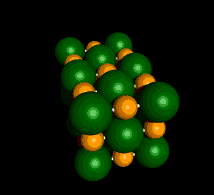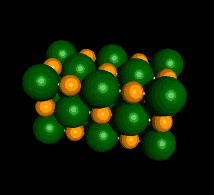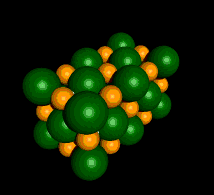 Sodium Chloride (NaCl)
Sodium Chloride (NaCl)
|
|





